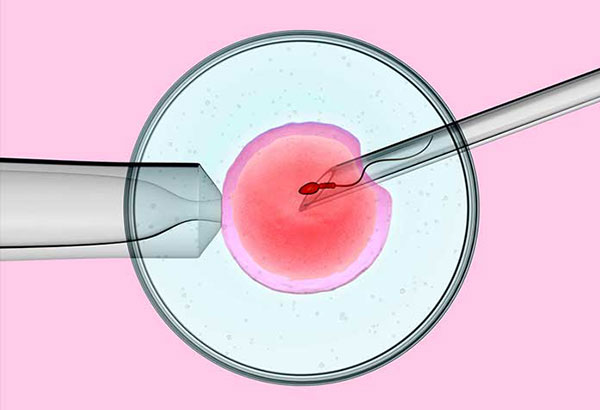
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection, which is also commonly known as ICSI is one of the common and most successful treatments for male fertility in Kandivali. This process is also performed by couples who were unsuccessful to fertilize during IVF. Sometimes some men need their sperm to be surgically extracted first. The process asks for the female partner to go through ovarian stimulation with the help of fertility medications. ICSI treatment can help to have a baby even if with low male sperm count issues. This process includes injecting the live sperm directly into the human egg.
During ICSI treatment the sperm doesn’t have to travel to the egg or penetrate the outer layers of the egg. Your doctor may recommend ICSI if there is any difficulty in achieving fertilization due to male infertility factors. The factors include:
 Low sperm count
Low sperm count Poor sperm motility
Poor sperm motility Decreased ability of sperm to penetrate into the egg
Decreased ability of sperm to penetrate into the egg Previous unsuccessful IVF procedure
Previous unsuccessful IVF procedureICSI works almost exactly like the IVF procedure, except the fertilization process. In IVF the fertilization process happens in a disc but in ICSI the sperm is injected into the egg individually using a machine called a micromanipulator.
You may have a higher risk of congenital conditions in your baby. During natural conception, only the hardiest sperm manage to break through the membrane of an egg to fertilize it. Weaker sperm doesn’t make it. But because ICSI treatment bypasses this natural selection process, there’s an increased risk of rare genetic problems carried by the sperm being passed on to the child. Some but not all genetic problems can be tested for before you have the treatment.
Finding from some but not all studies suggest that ICSI is associated with an increased risk for chromosomal abnormalities, autism, intellectual disabilities, and birth defects compared with conventional IVF. These increased risks may also be due to the effect of subfertiltiy.